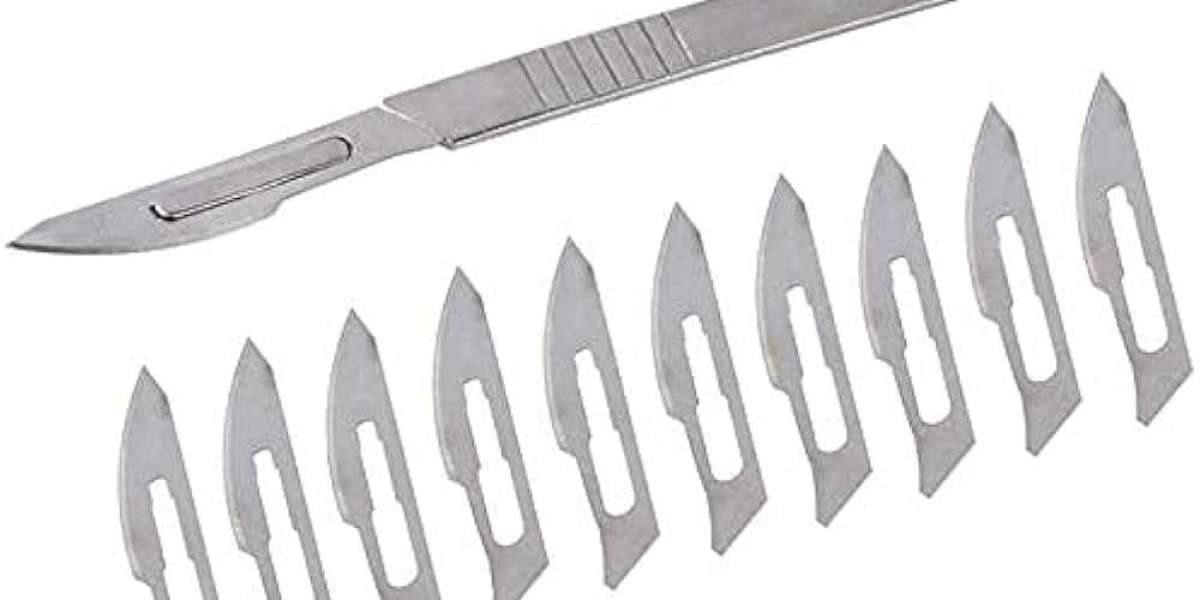
Surgical blades are indispensable tools in the medical field, playing a crucial role in procedures that demand precision and accuracy. However, the very nature of these sharp instruments also introduces significant risks to healthcare professionals if not handled properly. Adopting best practices in surgical blade safety and handling is essential to minimize accidents, ensure sterile environments, and promote efficient surgical procedures.
This comprehensive guide outlines the essential aspects of surgical blade safety, from proper handling techniques to disposal practices, ensuring that healthcare professionals are well-equipped to manage these tools effectively.
Importance of Surgical Blade Safety
Surgical blades, while vital for patient care, can be hazardous if not used, handled, or disposed of correctly. Mishandling a surgical blade can result in severe injuries, such as cuts or punctures, to the healthcare professional. These injuries not only compromise the safety of the medical staff but also pose risks of infection or exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
Furthermore, improper handling of surgical blades can lead to contamination, affecting the sterility of the surgical environment and potentially endangering the patient.
Key Reasons for Emphasizing Surgical Blade Safety
- Injury Prevention: Reducing the risk of accidental cuts and puncture wounds for healthcare staff.
- Infection Control: Preventing cross-contamination and maintaining sterile conditions during surgeries.
- Efficiency in Operations: Proper handling techniques contribute to smoother surgical procedures and minimize disruptions caused by accidents.
Understanding and implementing proper blade safety procedures not only protects the surgical team but also contributes to better patient outcomes by maintaining a sterile environment.
Proper Handling Techniques for Surgical Blades
Effective handling of surgical blades requires precision, focus, and adherence to established safety protocols. Each phase of the blade’s use — from opening the package to disposal — demands careful attention to ensure both the safety of the user and the sterility of the blade.
Steps for Safe Handling
- Proper Opening of Blade Packaging: Surgical blades are typically packaged in sterile pouches. When opening the package, avoid touching the blade with your hands to prevent contamination. Use sterile forceps or blade holders to remove the blade.
- Blade Attachment to Handle: When attaching the blade to a surgical handle, always use a blade holder or instrument specifically designed for this purpose. Never use your fingers, as this can result in cuts and compromise sterility. The blade should snap securely onto the handle, ensuring it is properly attached before use.
- During Surgery: While using the blade, always be mindful of where the cutting edge is positioned. Communicate clearly with the surgical team to prevent accidental contact with the blade during the procedure. Avoid using excessive force, which can cause the blade to slip and result in injury.
- Changing Blades: If you need to change the blade during surgery, use a blade remover or a needle holder to safely detach the used blade from the handle. This prevents any direct contact with the sharp edge, reducing the risk of injury.
- Post-Use Blade Management: Once a blade is no longer needed, it should be handled as a hazardous instrument. Carefully place it into a designated sharps container for proper disposal.
By following these handling protocols, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of injuries and ensure that the blade remains sterile throughout its use.
Safe Disposal of Surgical Blades
One of the most critical aspects of surgical blade safety is proper disposal. Discarded surgical blades are classified as sharps, and if not disposed of correctly, they can cause accidental injuries and pose health risks.
Best Practices for Blade Disposal
- Use of Sharps Containers: Always dispose of used blades in puncture-resistant sharps containers. These containers should be clearly labeled, easily accessible, and placed at strategic locations within the surgical room to prevent improper disposal.
- Avoid Overfilling: Sharps containers must never be overfilled, as this increases the risk of injuries. Once the container reaches the recommended fill level (usually indicated by a line on the container), it should be sealed and replaced with a new one.
- Seal and Label Containers: When a sharps container is full, securely seal it and ensure it is properly labeled as biohazardous waste. Follow the hospital or clinic’s protocol for the disposal of biohazard materials, ensuring that blades are handled with care at every stage.
- Training on Disposal Protocols: All healthcare workers should receive thorough training on how to dispose of surgical blades and other sharps properly. Regular refresher courses help ensure that staff stay aware of best practices and any updates to disposal protocols.
Proper disposal of surgical blades not only protects healthcare professionals from injury but also ensures compliance with health and safety regulations that govern medical waste management.
Infection Control and Sterility Maintenance
Maintaining a sterile surgical environment is paramount to patient safety. Surgical blades must be kept sterile before use to prevent infection. Any contamination of the blade can lead to complications such as infections, delayed healing, or even life-threatening conditions in the patient.
Strategies for Ensuring Blade Sterility
- Single-Use Blades: Many surgical settings opt for disposable, single-use blades, which eliminate the risk of cross-contamination between patients. These blades come pre-sterilized and are discarded immediately after use.
- Proper Handling to Maintain Sterility: During blade installation and use, touch only the blade’s handle or use sterile instruments to manipulate the blade. At no point should the cutting edge come into contact with non-sterile surfaces.
- Sterilization of Reusable Blades: For blades that are reusable, strict sterilization procedures must be followed. Autoclaving, chemical sterilization, and gamma radiation are commonly used methods. Each blade should be thoroughly inspected after sterilization to ensure it remains free of contaminants.
- Minimizing Blade Exposure: Once a blade is attached to a handle, minimize its exposure to non-sterile environments. If a blade is not immediately used after preparation, it should be covered or protected to prevent accidental contamination.
Proper sterilization and infection control measures protect both the patient and healthcare providers, reducing the likelihood of post-operative complications and improving overall surgical success rates.
Education and Training on Surgical Blade Safety
To promote safe handling and prevent accidents, comprehensive education and training programs are essential. Healthcare professionals must be familiar with the latest safety protocols and best practices for managing surgical blades.
Key Components of Blade Safety Training
- Proper Blade Handling Techniques: Training should cover all aspects of blade handling, from removal from packaging to disposal. This includes hands-on demonstrations of how to safely attach and remove blades from handles using specialized tools.
- Emergency Procedures for Blade Injuries: In the event of a blade-related injury, immediate action is necessary. Healthcare professionals should be trained in how to properly treat and report any injuries caused by surgical blades.
- Refresher Courses and Continuing Education: Safety training is not a one-time event. Regular refresher courses ensure that all surgical staff are up to date with the latest safety practices and technological advancements in blade handling.
By incorporating comprehensive training programs, healthcare institutions can reduce the number of blade-related injuries and promote a safer work environment for their staff.
Conclusion
Surgical blade safety and proper handling are crucial to protecting healthcare professionals and ensuring optimal patient outcomes. From safe handling techniques to secure disposal and sterilization practices, the responsibility for managing these sharp tools lies in the hands of trained professionals. By adhering to established safety protocols and continuing education efforts, medical teams can minimize risks and maintain a sterile, efficient surgical environment.
In summary, a combination of proper blade handling, effective disposal methods, rigorous infection control, and comprehensive training programs can significantly reduce the potential hazards associated with surgical blades. These efforts ultimately lead to safer, more efficient surgeries and better outcomes for patients and healthcare providers alike.