The global automotive turbocharger market size reached a value of above USD 13.31 billion in 2023. The industry is further expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.4% in the forecast period of 2024-2032 to reach a value of more than USD 32.21 billion by 2032. Turbochargers have become integral components in modern automotive engines, significantly enhancing performance while improving fuel efficiency. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of turbocharging technology, exploring its evolution, functionality, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
I. The Basics of Turbocharging
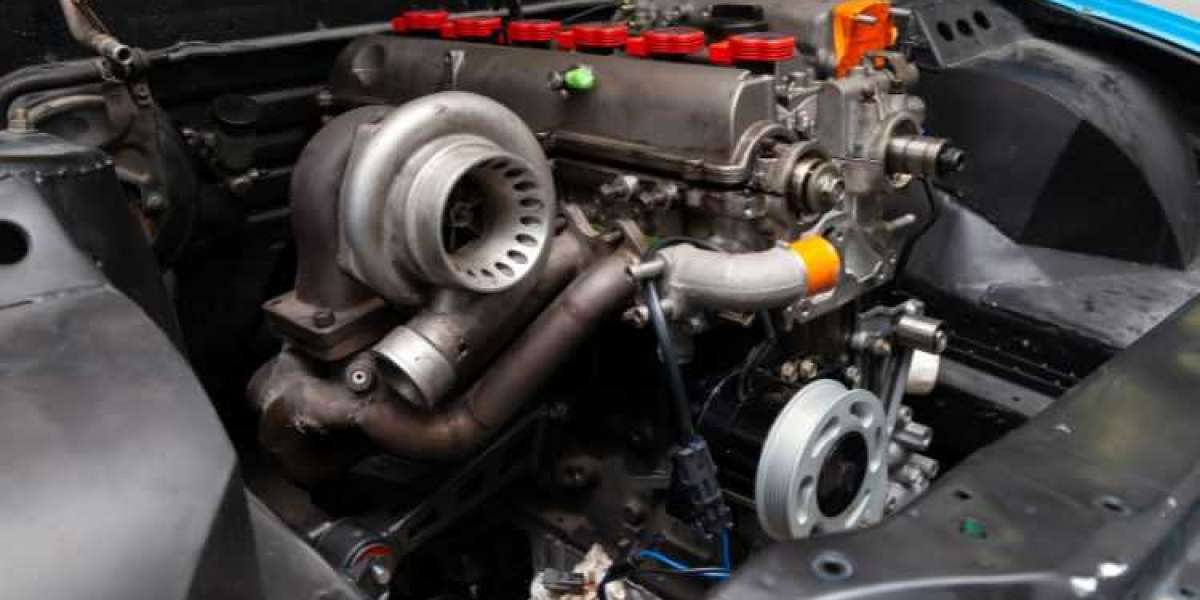
Turbocharging is a method of increasing an engine's power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. At its core, a turbocharger consists of two main components: a turbine and a compressor. The turbine is driven by exhaust gases expelled from the engine, while the compressor pressurizes the intake air before it enters the combustion chamber. This process, known as forced induction, allows the engine to produce more power than it would naturally aspirated.
II. Evolution of Turbocharged Engines
The history of turbocharging dates back to the early 20th century, but it wasn't until the 1960s that turbochargers gained popularity in the automotive industry. Saab and General Motors were among the first to adopt turbocharging in production vehicles, with models like the Saab 99 Turbo and Chevrolet Corvair Monza. Over the years, advancements in materials, design, and manufacturing have led to more efficient and reliable turbocharger systems.
III. Turbocharger Components and Technologies
Modern turbochargers are complex systems comprising various components, each playing a crucial role in performance enhancement.
A. Turbine and Compressor: These are the two main components of a turbocharger. The turbine is driven by exhaust gases, while the compressor pressurizes the intake air.
B. Wastegate: The wastegate regulates the boost pressure by controlling the flow of exhaust gases to the turbine.
C. Intercooler: Intercoolers are used to cool the compressed air before it enters the engine, increasing its density and improving performance.
D. Advanced Technologies: Innovations such as variable geometry turbochargers (VGT) and electric turbochargers have further optimized turbocharging technology, providing better responsiveness and efficiency across a wide range of engine speeds.
IV. Performance Enhancements with Turbochargers
One of the primary benefits of turbocharging is the significant increase in horsepower and torque. By compressing the intake air, turbochargers allow engines to burn more fuel, resulting in higher power output. This translates to improved acceleration, especially at low and mid-range RPMs, where turbocharged engines excel. Furthermore, turbochargers enhance engine efficiency by maximizing the air-fuel mixture's combustion, leading to better fuel economy compared to naturally aspirated engines of similar power output.
V. Challenges and Considerations
Despite their numerous advantages, turbochargers also pose certain challenges.
A. Turbo Lag: Turbo lag, the delay in throttle response due to the time required for the turbocharger to spool up, can be a significant drawback, especially in high-performance applications.
B. Reliability Issues: The increased stress and heat generated by turbocharging can impact engine reliability and longevity if not properly managed. Regular maintenance and monitoring of turbocharger components are essential to prevent issues such as oil leaks, bearing wear, and compressor surge.
VI. Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, turbocharging technology is expected to continue evolving to meet the demands of stricter emissions regulations and the growing shift towards electrification.
A. Research and Development: Manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development to improve turbocharger efficiency, reduce turbo lag, and integrate turbochargers with hybrid and electric powertrains seamlessly.
B. Advanced Designs: Variable geometry turbochargers, electric turbochargers, and integrated exhaust manifold designs are some of the innovations poised to shape the future of turbocharged engines.