Introduction
The telecommunications industry has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, with the demand for high-speed internet and efficient data transmission growing rapidly. Fiber optic cables, known for their ability to transmit large amounts of data at high speeds over long distances, have become a cornerstone of modern communication systems. This Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing Plant Project Report aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing process, market potential, investment requirements, and operational considerations for setting up a fiber optic cable manufacturing facility.
What Are Fiber Optic Cables?
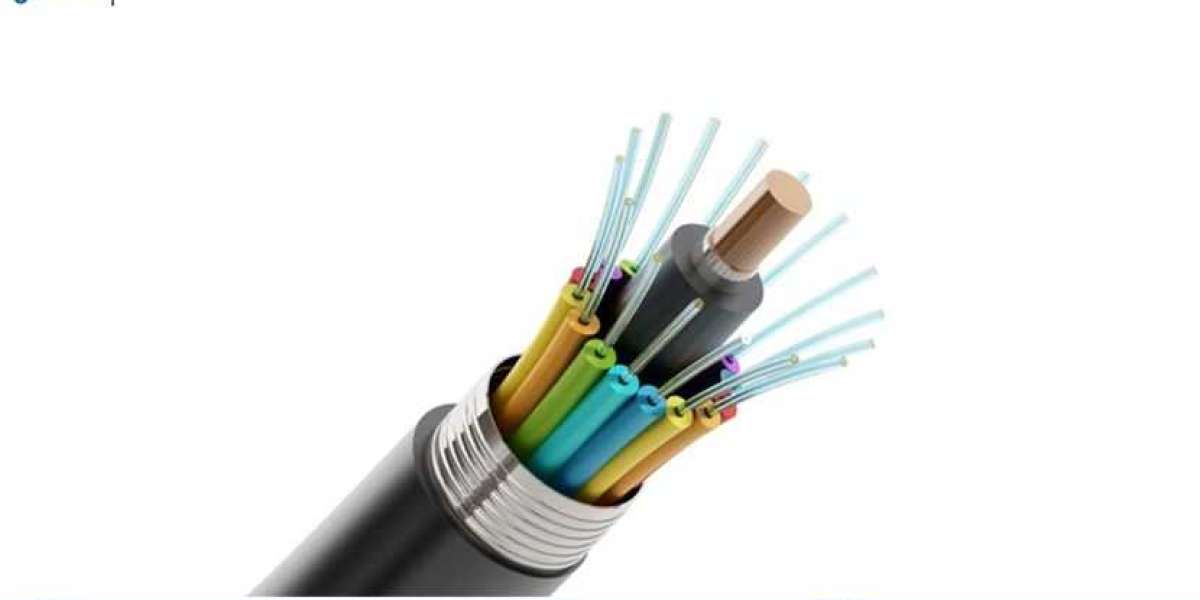
Fiber optic cables are composed of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that transmit light signals, enabling high-speed data transfer. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, allowing for clearer and faster communication. They come in two main types:
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF): Designed for long-distance communication, single-mode fibers have a small core diameter that allows only one mode of light to propagate, minimizing signal loss.
Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF): With a larger core diameter, multi-mode fibers can carry multiple light modes, making them suitable for shorter distances, such as within buildings or data centers.
Market Demand for Fiber Optic Cables
The fiber optic cable market has been experiencing robust growth due to several factors:
Increased Internet Traffic: The exponential growth of internet usage, streaming services, and online applications has created a surge in demand for high-speed data transmission.
5G Technology Rollout: The implementation of 5G technology requires extensive fiber optic networks to support faster data speeds and reduced latency.
Telecom Infrastructure Development: Governments and private companies are investing heavily in developing telecommunication infrastructure, including fiber optic networks, to improve connectivity.
Rise of Smart Cities: The development of smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT) necessitates reliable and high-speed communication networks, further driving demand for fiber optic cables.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents @
Benefits of Setting Up a Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing Plant
Growing Market Potential: As digital communication continues to evolve, the demand for fiber optic cables is expected to grow significantly, providing manufacturers with a lucrative market opportunity.
High Profit Margins: Given the increasing demand and technological advancements, manufacturers can expect healthy profit margins, especially if they can provide high-quality products.
Diverse Applications: Fiber optic cables are used in telecommunications, data centers, medical equipment, and military applications, ensuring a broad customer base.
Sustainability: Fiber optic cables are environmentally friendly as they consume less energy compared to traditional copper cables and have a longer lifespan.
Raw Materials Required for Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing
The production of fiber optic cables involves several key raw materials, including:
Silica Glass or Plastic Rods: The primary material for manufacturing fiber optic cores, silica glass is preferred for its low attenuation and high clarity.
Cladding Material: Usually made of lower refractive index glass or plastic, cladding surrounds the core to facilitate total internal reflection.
Protective Coatings: Polymer coatings provide protection against environmental factors and physical damage.
Buffer Tubes and Jackets: These materials protect the fibers from moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
Adhesives and Sealants: Used for bonding components during the assembly process.
Manufacturing Process of Fiber Optic Cables
The manufacturing process of fiber optic cables involves several stages, which can be summarized as follows:
Preform Fabrication: The first step in manufacturing fiber optic cables is creating a preform, which is a solid glass rod made of silica. This is done through a process called chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or outside vapor deposition (OVD), where silica is deposited layer by layer.
Drawing: The preform is heated in a furnace and drawn into thin fibers. This process involves pulling the preform down into a long, thin strand, typically 125 microns in diameter for single-mode fibers.
Coating: The drawn fiber is coated with a protective layer to enhance durability and prevent damage from environmental factors. This is typically done using a UV-curable polymer.
Testing: The fibers are tested for optical performance, including attenuation and bandwidth, to ensure they meet industry standards.
Buffering and Jacketing: The coated fibers are placed in buffer tubes, which are then surrounded by protective jackets made from materials like PVC or polyethylene to provide additional protection.
Assembly: The final step involves assembling the fibers into cables, which may include additional features such as strength members or water-blocking elements for added durability.
Machinery Required for Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing
Setting up a fiber optic cable manufacturing plant requires specific machinery and equipment, including:
Preform Fabrication Equipment: For creating silica preforms using CVD or OVD techniques.
Fiber Drawing Tower: A system for heating and drawing the preform into thin fibers.
Coating Machine: Equipment for applying protective coatings to the fibers.
Testing Equipment: For assessing the optical performance of the fibers.
Buffering and Jacketing Machinery: For assembling the fibers into protective cables.
Quality Control Instruments: To monitor and ensure compliance with industry standards throughout the manufacturing process.
Financial Aspects: Investment and Profitability
The investment required to set up a Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing Plant varies depending on the scale of operations, technology used, and location. Major cost components include:
Machinery and Equipment: The purchase and installation of specialized equipment can range from $500,000 to several million dollars.
Raw Materials: Consistent supply of raw materials such as silica glass, cladding material, and protective coatings is critical.
Labor Costs: Skilled labor is necessary for managing operations and overseeing production processes.
Utilities: The cost of electricity, water, and other utilities required for manufacturing.
Infrastructure: Investment in constructing the manufacturing facility and necessary storage areas.
Profitability margins in the fiber optic cable manufacturing sector can be substantial, often ranging from 15% to 25%, depending on market demand, production efficiency, and product quality.
Market Potential and Target Industries
The global fiber optic cable market is poised for significant growth, driven by demand across various sectors. Some key target markets include:
Telecommunications Industry: The primary consumer of fiber optic cables, with continued investments in infrastructure and networks.
Data Centers: Increasing data consumption and cloud computing services drive the need for high-speed connections within and between data centers.
Medical Equipment: Fiber optics are widely used in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment, such as endoscopes.
Military and Aerospace: The demand for secure and efficient communication systems in defense and aerospace applications further expands market potential.
Industrial Automation: As industries adopt automation and IoT technologies, the need for reliable communication networks grows.
Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with regulatory standards is crucial for manufacturers of fiber optic cables. Key regulations include:
- ISO Certifications: Obtaining ISO 9001 for quality management systems ensures that products meet international standards.
- Environmental Regulations: Adhering to environmental standards for waste disposal and emissions control is essential for sustainable operations.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with electrical and safety standards is necessary to ensure the safety of manufacturing processes and products.
FAQ
What are fiber optic cables?
Fiber optic cables consist of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that transmit light signals for high-speed data communication.What raw materials are required for fiber optic cable manufacturing?
Key raw materials include silica glass or plastic rods, cladding materials, protective coatings, buffer tubes, and jackets.What are the main types of fiber optic cables?
The two main types are single-mode fiber (SMF) for long distances and multi-mode fiber (MMF) for shorter distances.How much investment is required to set up a fiber optic cable manufacturing plant?
Initial investments can range from $500,000 to several million dollars, depending on the scale of production and technology used.What are the profit margins in fiber optic cable manufacturing?
Profit margins typically range from 15% to 25%, depending on production efficiency and market demand.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/fencing-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/aerospace-coatings-marke
thttps://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/camping-tent-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au