Introduction: The Convergence of Industrial Agriculture and Ethical Concerns
In the modern era, factory farming has become a cornerstone of agricultural efficiency and productivity. This system of industrialized agriculture, designed to maximize output and reduce costs, has dramatically transformed food production worldwide. However, the rise of factory farming has also sparked a profound ethical debate surrounding animal rights. This article explores the intersection of factory farming and animal welfare, shedding light on the moral considerations and implications of this industrial approach to agriculture.
Understanding Factory farming and animal rights
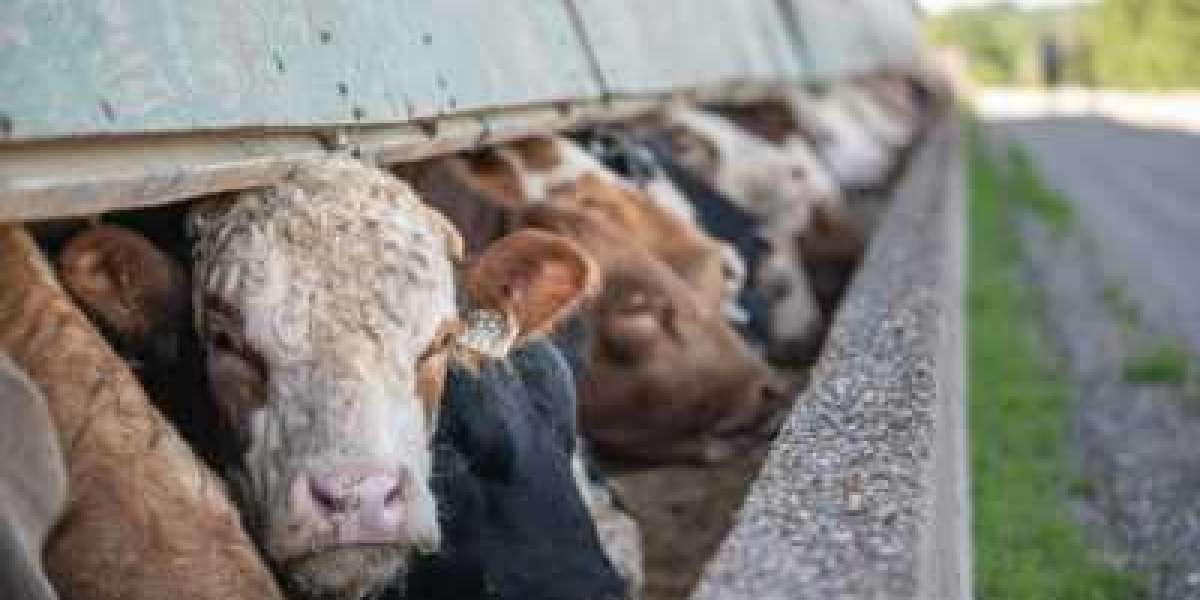
Factory farming refers to the intensive production of livestock in confined spaces, aimed at producing large quantities of meat, dairy, and eggs at minimal cost. This system relies on technologies and practices designed to optimize efficiency, such as controlled environments, automated feeding, and rapid growth cycles. While factory farming has contributed to lower food prices and increased availability, it has also raised significant concerns regarding animal welfare.
The Ethical Issues: A Closer Look at Animal Welfare
Central to the animal rights debate is the treatment of animals within factory farms. Critics argue that the conditions in which animals are raised, confined, and slaughtered are inhumane. Key ethical issues include:
- Confinement and Lack of Space: Animals in factory farms are often kept in overcrowded conditions with limited space to move. For instance, pigs are frequently housed in gestation crates, and chickens are kept in battery cages. These restrictive environments can lead to physical and psychological distress, affecting the animals' well-being.
- Health and Well-Being: The rapid growth promoted by factory farming practices can result in health problems for animals. For example, fast-growing poultry may suffer from skeletal issues, and dairy cows might experience chronic lameness. Additionally, the use of antibiotics and hormones raises concerns about both animal health and potential human health implications.
- Ethical Treatment and Slaughter: The process of slaughter in factory farms often involves methods designed to maximize efficiency, which can sometimes result in less humane treatment of animals. Issues such as pre-slaughter handling, stunning, and killing methods are critical points of contention among animal rights advocates.
Animal Rights Perspectives: Philosophical and Practical Considerations
The debate over factory farming and animal rights is deeply rooted in philosophical questions about the moral status of animals. Various perspectives contribute to the discourse:
- Utilitarianism: Utilitarian philosophers argue that the suffering of animals in factory farms outweighs the benefits of industrialized meat production. According to this view, the ethical course of action would involve reducing animal suffering, which might include adopting more humane farming practices or reducing meat consumption.
- Deontological Ethics: From a deontological perspective, certain actions are inherently wrong regardless of their consequences. This approach might argue that factory farming is unethical due to the inherent violation of animals' rights to live free from harm and exploitation.
- Animal Liberation: Advocates for animal liberation assert that animals have intrinsic rights and should not be used as commodities. This perspective often calls for a complete overhaul of factory farming practices and the promotion of alternatives, such as plant-based diets or more humane farming methods.
Regulatory and Reform Efforts: Moving Towards a More Ethical Future
In response to growing concerns about animal welfare, there have been efforts to reform factory farming practices and improve conditions for animals. Some notable developments include:
- Legislation and Welfare Standards: Various countries and regions have enacted laws aimed at improving animal welfare in factory farms. For example, the European Union has established regulations on the minimum standards for animal housing, while certain U.S. states have passed measures to ban or restrict the use of specific confinement systems.
- Corporate and Consumer Initiatives: Many companies and consumers are increasingly prioritizing ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions. This shift has led to the rise of certified humane labels, such as those from the Humane Society International or the Global Animal Partnership, which indicate higher welfare standards.
- Advocacy and Public Awareness: Organizations and activists continue to raise awareness about the conditions in factory farms and advocate for change. Campaigns, documentaries, and social media initiatives play a crucial role in informing the public and driving demand for more ethical food production practices.
Conclusion: The Path Forward in the Factory Farming Debate
The ethical dilemma of Factory farming and animal rights presents a complex challenge that requires careful consideration of both practical and moral dimensions. As society grapples with the consequences of industrial agriculture, it is essential to engage in meaningful dialogue, support reforms, and explore alternative approaches to food production. By addressing the concerns raised by factory farming, we can work towards a more humane and sustainable future for both animals and humans.